Graphite Electrode Industry Trends: Market Dynamics, Technological Advancements, and Future Outlook
2025.4.9
Graphite electrodes, a critical material in electric arc furnace (EAF) steelmaking, industrial silicon, yellow phosphorus smelting, and lithium-ion battery anode production, have experienced significant market fluctuations and technological advancements in recent years. Driven by global carbon neutrality policies, the rise of the new energy sector, and the transformation of the steel industry, the graphite electrode market is undergoing profound changes. This article provides an in-depth analysis of the latest industry trends, covering global supply and demand, price movements, technological developments, and future prospects.

2.Global Supply and Demand Analysis
2.1 Demand Side: Growth Driven by EAF Steelmaking and New Energy Industries
- EAF Steelmaking Demand Growth:
With the global push toward “carbon neutrality,” short-process steelmaking (EAF) has become a key focus for the steel industry due to its lower carbon emissions (~70% less CO₂ compared to blast furnace-BOF routes). Government policies in China, the EU, and India are supporting EAF adoption, boosting graphite electrode demand. According to CRU, global graphite electrode demand reached ~1.2 million tons in 2023 and is expected to rise to 1.4 million tons by 2025. - New Energy Industry Demand:
The surge in lithium-ion battery anode (e.g., artificial graphite) production has increased demand for needle coke (a key raw material for electrodes), indirectly affecting supply dynamics. Additionally, steady growth in industrial silicon (for solar PV) and yellow phosphorus smelting further supports demand.
2.2 Supply Side: China Dominates Production, Overseas Players Adjust Strategies
Overseas Producers Scale Back or Shift Focus:
U.S.-based GrafTech and Germany’s SGL are exiting certain markets due to cost pressures, pivoting toward high-end specialty graphite (e.g., large-diameter ultra-high-power electrodes).
China Accounts for Over 70% of Global Capacity:
Companies such as Fangda Carbon, Jilin Carbon, and Nantong Yangzi continue to expand production. China’s graphite electrode capacity exceeded 1.5 million tons in 2023, but environmental restrictions and volatile needle coke prices have kept operating rates at ~60-70%.
3. Price Trends and Raw Material Volatility
3.1 Needle Coke Supply Crunch Drives Up Costs
The price of needle coke (petroleum- or coal-based), a key electrode feedstock, is heavily influenced by oil and coal tar pitch prices. In 2023, petroleum-based needle coke prices exceeded ¥8,000/ton, pushing up electrode production costs.
Competition from the lithium-ion battery anode industry for needle coke resources has further tightened supply.
3.2 Graphite Electrode Price Trends
In 2021-2022, ultra-high-power (UHP) electrode prices surged to 3,000−3,000−4,000/ton (in overseas markets) due to EAF demand recovery.
Post-2023, increased Chinese supply and weaker overseas demand led to a price correction to 2,000−2,000−2,500/ton, still above 2019 lows.
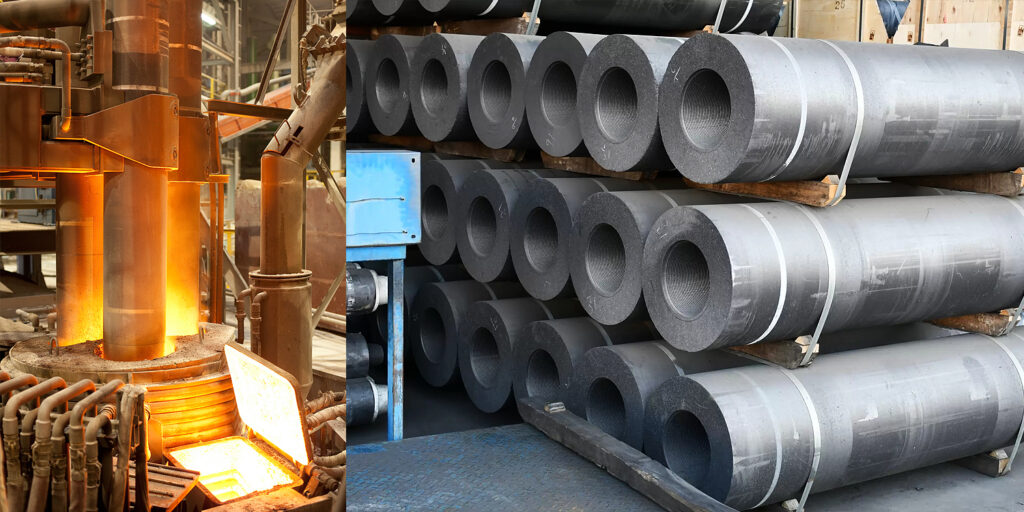

4. Technological Advancements and Innovations
4.1 Large-Size and Ultra-High-Power Electrodes Become Mainstream
- The trend toward larger EAFs has boosted demand for UHP electrodes with diameters exceeding 600mm, requiring higher density and thermal shock resistance.
- Chinese manufacturers have made breakthroughs in 30-inch (762mm) electrode technology, gradually replacing imports.
4.2 Eco-Friendly and Energy-Efficient Production
- Optimized Baking Processes:
Closed-loop ring furnaces reduce energy consumption and emissions. - Recycling of Waste Electrodes:
Crushing and regeneration technologies can cut raw material costs by 15-20%, aligning with circular economy trends.
4.3 Specialty Graphite Electrodes Expand into New Applications
- High-purity graphite (ash content <0.1%) is increasingly used in semiconductors and nuclear energy, with Japanese firms like Tokai Carbon dominating this niche.
5. Policy and Challenges
5.1 Stricter Environmental Regulations
- China’s “dual carbon” goals classify graphite electrode production as energy-intensive, leading to production caps in some regions. The EU’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) may raise export costs.
5.2 Trade Dispute Risks
- Anti-dumping investigations in India, Turkey, and other markets are prompting Chinese firms to establish overseas production (e.g., Fangda Carbon’s Turkey project).
6. Future Outlook
Technology-Driven Competition:
High-end products (e.g., coated electrodes, high-density electrodes) will become key profit drivers.
Sustained Demand Growth:
The global EAF steel share is projected to rise from 28% in 2023 to 35% by 2030, supporting long-term electrode demand.
Industry Consolidation Accelerates:
Smaller players face exit due to environmental and cost pressures, while leading firms expand through M&A.